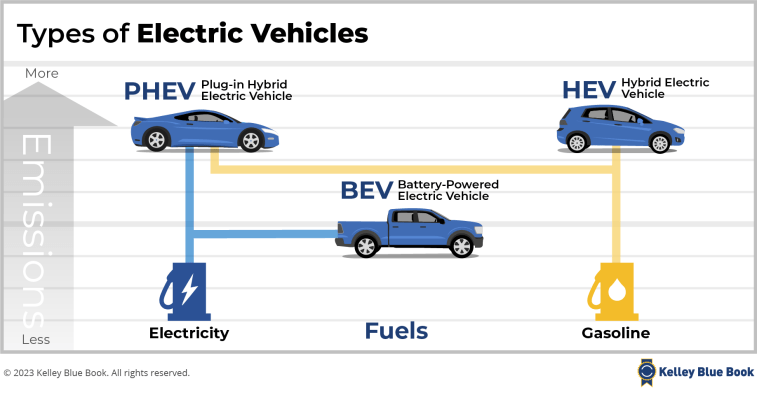
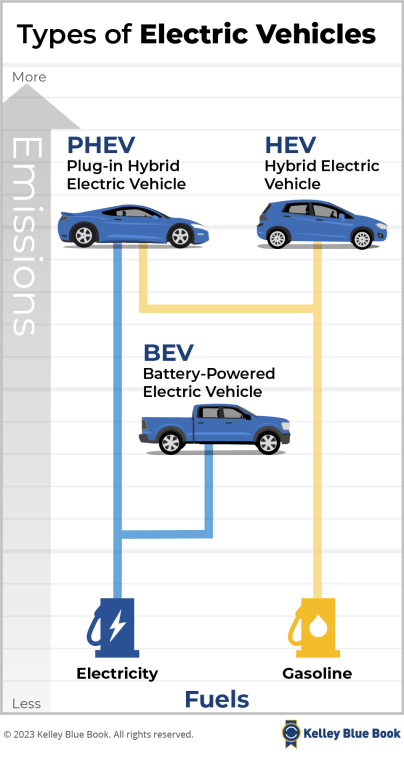
Quick Facts About Federal Incentives for Electric Cars
- Starting Jan. 1, 2024, stricter rules take effect that will limit EVs eligible for federal tax credits.
- For EVs that qualify, consumers can instantly obtain tax credits of up to $7,500 off qualifying new vehicles and $4,000 off used vehicles. Those credits can be used as car down payments.
- The list of eligible electric vehicles is not yet published. However, it’s slated to be a smaller number in 2024 due to battery and parts requirements.
- Income caps on the electric car tax credit eligibility still apply.
Consumers considering a new electric vehicle or plug-in hybrid might want to act fast. With incentives potentially running out on Jan. 1, 2024, car shoppers should weigh how tax credits work and how they could affect any upcoming buying decisions.
Read on to find out if federal tax incentives will help you defray the cost of buying a zero-emission vehicle when combined with state and local rebates.
How the New EV Tax Credits Work
According to Kelley Blue Book research, electric car buyers spent $52,345 on average for a new EV purchase in November, down more than $10,000 since a year ago. The industry-wide average that includes gas-powered vehicles and electric cars reached $48,247 in the same time frame.
Here’s how the electric vehicle tax credits work in 2023 and 2024 (as of this writing):
- Discount up front. In 2024, dealerships can offer instant EV tax rebates to qualifying customers on qualifying vehicles who can use them as down payments at the time of purchase. You can still request the credit on your taxes. See the full list below.
- Credits up to $7,500. The Inflation Reduction Act allows up to $7,500 in tax credits for select new electric cars, plug-in hybrids, and hydrogen-powered vehicles that meet government qualifications. The federal government continues to update the list of qualifying vehicles.
- Caps EV price tags. The incentives restrict qualifying vehicles to low-emissions trucks, SUVs, and vans with manufacturer’s suggested retail prices (MSRPs) of up to $80,000 and cars up to $55,000.
- Income caps to qualify for new cars. The rebates are limited to individuals reporting adjusted gross incomes of $150,000 or less on taxes, $225,000 for those filing as head of household, and $300,000 for joint filers.
| IRS Tax Filing Status | Adjusted Gross Income Limits |
| Single | $150,000 |
| Head of household | $225,000 |
| Married and filing jointly | $300,000 |
| Married and filing separately | $150,000 |
- Used electric vehicle rebate. Anyone considering a used electric car under $25,000 could obtain up to a $4,000 tax credit, subject to income and other limits. To qualify, used cars must be at least two model years old. The vehicle also must be purchased at a dealership. The vehicle also only qualifies once in its lifetime. Purchasers of used vehicles can only qualify for one credit every three years, and to qualify, individuals must meet income requirements (see below). The credit ends in 2032.
| IRS Tax Filing Status | Adjusted Gross Income Limits |
| Single | $75,000 |
| Head of household | $112,500 |
| Married and filing jointly | $150,000 |
| Married and filing separately | $75,000 |
- Leased vehicles may qualify. The IRS lets dealers claim credits of up to $7,500 on cars available for lease. Dealers, in turn, can apply that amount to the price of the vehicle before setting lease terms, effectively lowering the cost to shoppers.
- No sales limits for manufacturers. As of Jan. 1, 2023, manufacturers like GM and Tesla were no longer limited on incentives to the first 200,000 EVs sold, which was the case under previous federal tax credits.
- Ineligible cars become eligible. Carmakers like Tesla and General Motors, which had run out of available credits under the old plan, became eligible for them again as of January 2023.
- New rules on EV battery manufacturing. To qualify for the subsidy, electric car batteries must have final assembly in the United States, Canada, or Mexico, and the batteries’ minerals and parts must also come from North America to qualify. These rules render many electric vehicles ineligible. The U.S. Treasury Department recently updated regulations that govern where battery minerals and parts must be sourced. A new list of vehicles published on April 18 says that cars qualify for a $3,750 benefit if the assembly of at least half the value of their battery components happens in North America. Cars qualify for a second $3,750 incentive if critical minerals used in the batteries, like cobalt and lithium, originate in the U.S. or its free-trade partners. Currently, the rules require 40% of battery content from such countries. In 2024, that number will increase to 50% and ladder up to 80% in 2027. The department will use a similar, 3-part test to decide whether cars have met mineral standards.
- Hydrogen fuel-cell cars remain eligible. Hydrogen fuel-cell cars like the Toyota Mirai or Hyundai Nexo qualify for $4,500 in incentives. However, those make sense only for buyers in California who live near one of America’s few hydrogen refueling stations. Those stations are mostly concentrated in California. Read our article about the pros and cons of hydrogen fuel-cell cars.
- Home electric car chargers and installation costs get a rebate. Federal incentives include a 30% tax credit up to $1,000 for electric car chargers and installation costs. The tax credit extends through Dec. 31, 2032. To claim your credit, use IRS form 8911 and file with your federal tax returns.
List of 2023-2024 Electric Vehicles That Qualify
The U.S. Internal Revenue Service has yet to release its newest list. So far, we know the following updates to the tax credits for Jan. 1, 2024.
- Chrysler Pacifica plug-in hybrid will continue to get a $7,500 tax credit.
- Tesla Model 3 Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) and Long Range trims will no longer qualify for the federal EV tax credits after Dec. 31.
- Ford Mustang Mach-E is reportedly off the list.
- GM told us earlier this year, the company would halt Bolt production at the end of 2023.
Once the IRS publishes its new list of qualifying vehicles, we will update ours.
Here’s the list of vehicle that qualify on or after April 18, 2023 to Dec. 31, 2023. The list constantly changes as car manufacturers open assembly plants in the U.S. to meet the new requirements.
| Vehicle | Credit Amount | MSRP Limit |
| 2024 BMW xDrive50e PHEV | $3,750 | $80,000 |
| 2023-2024 Cadillac Lyriq | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2024 Chevrolet Blazer EV | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Chevy Bolt EV | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2023 Chevy Bolt EUV | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2024 Chevy Equinox EV | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2024 Chevy Silverado EV | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023-2024 Chrysler Pacifica PHEV | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Ford E-Transit | $3,750 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Ford Escape PHEV | $3,750 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Ford F-150 Lightning | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Ford Mustang Mach-E | $3,750 | $80,000 |
| 2023-2024 Jeep Grand Cherokee 4xe PHEV | $3,750 | $80,000 |
| 2023-2024 Jeep Wrangler 4xe PHEV | $3,750 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Lincoln Aviator Grand Touring | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Lincoln Corsair Grand Touring | $3,750 | $80,000 |
| 2024 Nissan Leaf S | $3,750 | $55,000 |
| 2024 Nissan Leaf SV Plus | $3,750 | $55,000 |
| 2023 Rivian R1S | $3,750 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Rivian R1T | $3,750 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Tesla Model 3 Standard Range RWD | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2023 Tesla Model 3 Performance | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2023 Tesla Model 3 Long Range AWD | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2023 Tesla Model X Long Range | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Tesla Model Y AWD | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Tesla Model Y Long Range AWD | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Tesla Model Y Performance | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Tesla Model Y RWD | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Volkswagen ID.4 | $7,500 | $80,000 |
UPDATE: Recent Tesla price cuts on the base Model S may allow those vehicles to qualify for government tax credits. According to Tesla’s website, some buyers can qualify for the full $7,500 EV tax credit on the base Model S, which is priced at $74,990 now, down from $104,990 on Jan. 1. The government’s list of qualifying vehicles does not yet list the Model S among qualifying cars.
This is the list of electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles that qualify for tax credits if placed in service between Jan. 1, 2023, and April 17, 2023.
| Vehicle | Credit Amount | MSRP Limit |
| 2023 Audi Q5 TFSI e Quattro PHEV | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2021-2023 BMW 330e PHEV | $5,836* | $55,000 |
| 2021-2023 BMW X5 eDrive 45e PHEV | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2024 Cadillac Lyriq | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Chevy Bolt EV | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2022-2023 Chevy Bolt EUV | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2024 Chevy Silverado EV | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Chrysler Pacifica PHEV | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Ford E-Transit | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022 Ford Escape PHEV | $6,843 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Ford Escape PHEV | $6,885 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Ford F-150 Lightning | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Ford Mustang Mach-E | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023-2024 Genesis Electrified GV70 | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Jeep Grand Cherokee 4xe PHEV | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Jeep Wrangler 4xe PHEV | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Lincoln Aviator Grand Touring PHEV | $6,534 | $80,000 |
| 2022 Lincoln Corsair Grand Touring PHEV | $6,843 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Lincoln Corsair Grand Touring PHEV | $6,885 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Mercedes-Benz EQE | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2021-2023 Nissan Leaf S | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2021-2022 Nissan Leaf S Plus | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2021-2022 Nissan Leaf SL Plus | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2021-2022 Nissan Leaf SV | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2021-2023 Nissan Leaf SV Plus | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2022-2023 Rivian R1S | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Rivian R1T | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Tesla Model 3 Long Range | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2022-2023 Tesla Model 3 Performance | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2022-2023 Tesla Model 3 RWD | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2022-2023 Tesla Model Y AWD | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Tesla Model Y Long Range | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022-2023 Tesla Model Y Performance | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2023 Volkswagen ID.4 | $7,500 | $80,000 |
| 2022 Volvo S60 PHEV | $5,419 | $55,000 |
| 2022 Volvo S60 Extended Range PHEV | $7,500 | $55,000 |
| 2023 Volvo S60 T8 Recharge Extended Range PHEV | $7,500 | $55,000 |
*Check VIN to know if assembled in North America.
State and Local Incentives Near You
Though the federal government’s effort makes up the lion’s share of government EV discounts, some states and local governments offer incentive programs to help new car buyers afford something more efficient. These can be tax credits, rebates, reduced vehicle taxes, single-occupant carpool-lane access stickers, and registration or inspection fee exemptions.
States like California and Connecticut offer broad support for electric vehicle buyers. However, Idaho and Kentucky are among the states offering no support to individual EV buyers.
Your Electric Utility May Help
Lastly, it’s not just governments that can help you with the cost of a new EV. Some local electric utilities provide incentive programs to help buyers get into electric vehicles. After all, they’re among the ones that benefit when you turn your fuel dollars into electricity dollars.
Some offer rebates on cars. Others offer discounts on chargers or install them for free when you sign up for off-peak charging programs.
For example, Rhode Island offers up to $1,500 to residents who purchase or lease a qualified new battery electric vehicle. The state also rebates up to $1,500 more to purchasers who qualify based on income eligibility.
Electric Car Guides:
Editor’s Note: This article has been updated for accuracy since it was originally published.
This article was originally published by a www.kbb.com . Read the Original article here. .